Monte-Bianco
Size Range
Monte-Bianco Magnets Size Range and Inspection Standard
Table 1:General appearance inspection standards for block blanks
|
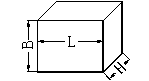
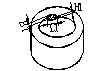
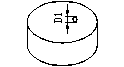
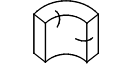
Schematic diagram of the block blank |
Size range (unit: mm) |
|||||
|
|
L: perpendicular to the pressing direction B: pressing direction H: magnetization direction |
|||||
|
30≤L≤40 |
40≤L≤60 |
60≤L≤90 |
90≤L≤150 |
|||
|
Defect Category |
Schematic diagram |
Defect limit conditions |
||||
|
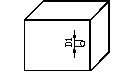
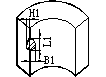
Plane gap |
|
L1≤1.2 B1≤1 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.7 B1≤1.5 H1≤1.2 |
L1≤2 B1≤1.6 H1≤1.5 |
|
|
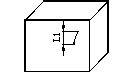
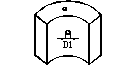
Impurities |
|
D1≤0.3 |
D1≤0.5 |
D1≤1 |
D1≤1.5 |
|
|
Internal crack |
|
Internal cracks are judged as unqualified |
||||
Table 2: General appearance inspection standards for ring blanks
|
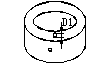
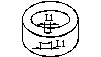
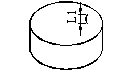
Schematic diagram of the shape of the ring blank |
Size range (unit: mm) |
||||
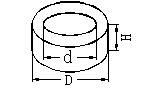 |
D: outer diameter of the ring d: inner diameter of the ring H: thickness (usually in the direction of magnetization) |
||||
|
60≤D≤80 |
80≤D≤100 |
100≤D≤120 |
120≤D≤140 |
||
|
Defect Category |
Schematic diagram |
Defect limit conditions |
|||
|
Outer arc missing corner |
|
L1≤1.2 B1≤1 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.7 B1≤1.5 H1≤1 |
L1≤2 B1≤1.6 H1≤1 |
|
Impurities |
|
D1≤0.5 |
D1≤0.8 |
D1≤1 |
D1≤1.5 |
|
Inner arc missing corner |
|
L1≤1.2 B1≤1 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.7 B1≤1.5 H1≤1 |
L1≤2 B1≤1.6 H1≤1 |
|
Internal crack |
|
Internal cracks are judged as unqualified |
|||
Table 3: General appearance inspection standards for cylindrical blanks
|
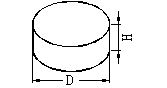
Schematic diagram of cylindrical blank shape |
Size range (unit: mm) |
||||
|
|
D: outer diameter of cylinder H: thickness (usually in the direction of magnetization) |
||||
|
10≤D≤20 |
20≤D≤40 |
40≤D≤60 |
60≤D≤80 |
||
|
Defect Category |
Schematic diagram |
Defect limit conditions |
|||
|
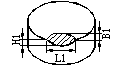
Missing corner |
|
L1≤1 B1≤1 H1≤0.8 |
L1≤1.2 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.8 B1≤1.5 H1≤1 |
|
Impurities |
|
D1≤0.3 |
D1≤0.5 |
D1≤0.8 |
D1≤1.2 |
|
Internal crack |
|
Internal cracks are judged as unqualified |
|||
Table 4: General appearance inspection standards for tile blanks
|
Schematic diagram of the appearance of the tile blank |
Size range (unit: mm) |
||||
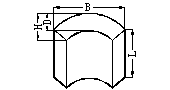 |
L: length B: width D: thickness H: arch height (D and H are generally the magnetization direction) |
||||
|
20≤L≤40 20≤B≤40 20≤H≤40 |
40≤L≤60 20≤B≤40 20≤H≤40 |
60≤L≤80 30≤B≤50 30≤H≤50 |
60≤L≤80 40≤B≤60 30≤H≤50 |
||
|
Defect Category |
Schematic diagram |
Defect limit conditions |
|||
|
Missing corner |
|
L1≤1 B1≤1 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.2 B1≤1 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1 |
L1≤1.5 B1≤1.2 H1≤1.2 |
|
Impurities |
|
D1≤0.3 |
D1≤0.5 |
D1≤0.8 |
D1≤1.2 |
|
Internal crack |
|
Internal cracks are judged as unqualified |
|||
Notes:
1. The above is the company's general qualification judgment standard for rough products. When this standard cannot meet customer requirements, it will be implemented according to customer standards (when customers have special requirements, they will be resolved through negotiation between the two parties.)
2. The name of the conventional appearance defect refers to "missing corners". If it is difficult to judge by visual inspection, it can be measured by caliper or projection to quantify the judgment in mm, or it can be judged by the missing corner volume/corresponding specification volume mm3 < 2%. After full communication with the customer, if the missing corner does not affect the magnetic flux, the magnetic flux can be used for the final judgment;
3. In addition to the above 4 common specifications, such as trapezoidal (converted by square), special-shaped products, etc., judge according to the close specifications;
NdFeB Plating Requirement
| Type of Coating | Type of CoatingThi ckness (jum) | Neutral SaltSpray Test (h) | Temperature & HumidityTest (h) |
PCT/HAST(h) | Operating Temperature (°C) |
|
| Zn(Bluish white) | 4~15 | ≤24 | / | / | ≤160 | |
| Zn(Colored) | 4~15 | ≤48 | / | / | ≤160 | |
| Ni(Barrel Plating) | 5~20 | ≤48 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| Ni(Rack Plating) | 5~20 | ≤16 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi(Barrel Plating) | 5~20 | ≤48 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi(Rack Plating) | 5~20 | ≤16 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| Epoxy | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤72 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+Epoxy | 10~30 | ≤500 | ≤500 | ≤200 | ≤160 | |
| NiCu+EpOXy | 10~30 | ≤500 | ≤500 | ≤200 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+Sn | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| Ni+Ag | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+AU | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi+Sn | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| Ni+AP.Ni(Barrel Plating) | 3~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+AP.Ni(Rack Plating) | 3~20 | ≤24 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| PVD.AI | 2~15 | ≤24 | ≤168 | ≤24 | ≤400 | |
| The specific corrosion resistance of different products depends on the productspecifications. in general,temperature & humidity test and PCT/HAST tests are not conducted | ||||||
Smco Plating Requirement
| Type of Coating | Type of CoatingThi ckness (jum) | Neutral SaltSpray Test (h) | Temperature & HumidityTest (h) |
PCT/HAST(h) | Operating Temperature (°C) |
|
| Zn(Bluish white) | 4~15 | ≤24 | / | / | ≤160 | |
| Zn(Colored) | 4~15 | ≤48 | / | / | ≤160 | |
| Ni(Barrel Plating) | 5~20 | ≤48 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| Ni(Rack Plating) | 5~20 | ≤16 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi(Barrel Plating) | 5~20 | ≤48 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi(Rack Plating) | 5~20 | ≤16 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤200 | |
| Epoxy | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤72 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+Epoxy | 10~30 | ≤500 | ≤500 | ≤200 | ≤160 | |
| NiCu+EpOXy | 10~30 | ≤500 | ≤500 | ≤200 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+Sn | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| Ni+Ag | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+AU | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| NiCuNi+Sn | 5~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤96 | ≤200 | |
| Ni+AP.Ni(Barrel Plating) | 3~20 | ≤72 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| Ni+AP.Ni(Rack Plating) | 3~20 | ≤24 | ≤168 | ≤48 | ≤160 | |
| PVD.AI | 2~15 | ≤24 | ≤168 | ≤24 | ≤400 | |
| The specific corrosion resistance of different products depends on the productspecifications. in general,temperature & humidity test and PCT/HAST tests are not conducted | ||||||